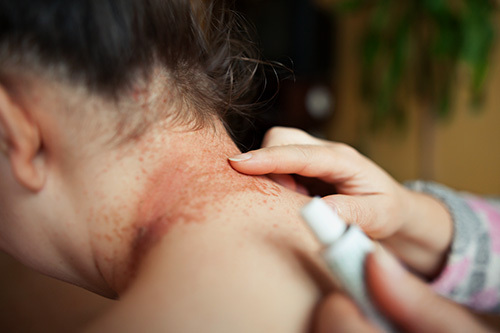
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that often requires long-term management rather than a one-time solution. While in-office care and prescription medications play an essential role, effective eczema treatment goes far beyond specialist appointments.
Daily habits, skin care routines, and informed at-home practices are important for maintaining healthy skin and reducing flares.*
Eczema treatment at home focuses on restoring the skin barrier, minimizing inflammation, and avoiding triggers that worsen symptoms. In many cases, prescription medications—such as topical steroids or nonsteroidal creams—are incorporated into a daily routine alongside moisturizers and lifestyle shifts. When done correctly, eczema home treatments can significantly improve comfort, reduce flare frequency, and support long-term disease control.
Eczema Treatment at Home
Managing eczema at home involves consistency and a careful approach to skin care. Both natural remedies for eczema and dermatologist-recommended practices can help soothe irritated skin and support healing. The goal is not to replace medical care, but to enhance it through safe, evidence-based home strategies.
Natural Treatment for Eczema
Many patients ask how to treat eczema naturally. While “natural” does not always mean risk-free, several well-studied options can be helpful when used appropriately.
Colloidal oatmeal
Colloidal oatmeal is widely recognized because of its anti-inflammatory and skin-soothing properties. It helps relieve itching and supports the skin barrier, making it a common ingredient in eczema-friendly baths and moisturizers.
Coconut oil
Virgin coconut oil has antimicrobial properties and can help lock in moisture. It may be beneficial for mild eczema when applied to intact skin, but it should be avoided if irritation occurs.
Sunflower seed oil
Sunflower seed oil supports the skin barrier and reduces inflammation. It is typically well-tolerated and can be used as a moisturizer for sensitive skin.
Petroleum jelly
Petroleum jelly is one of the most effective ways to seal in moisture. It creates a protective barrier that reduces water loss and is often recommended as a first-line moisturizer for eczema.
Cool compresses
Applying a cool, damp cloth to affected areas can momentarily reduce itching and inflammation, especially during active flares.
Tips for Eczema Management
Beyond specific remedies, daily habits play a significant role in eczema control.
Moisturize regularly
Frequent moisturizing—at least twice daily—is essential. Applying moisturizer immediately after bathing helps trap moisture in the skin.
Use fragrance-free products
Fragrances are a common trigger. Choose products labeled “fragrance-free” rather than “unscented,” which may still contain masking fragrances.
Avoid long, hot showers
Hot water strips the skin of natural oils. Opt for lukewarm showers and limit bathing time to 10–15 minutes.
Learn your triggers
Triggers vary from person to person and may include stress, allergens, fabrics, or certain foods. Observing patterns can help prevent flares.
Test new skin care products
Patch testing new products on a small area of skin can help prevent widespread irritation.
Protect skin from harsh weather
Cold air, wind, and low humidity can worsen eczema. Protective clothing and heavier moisturizers can help during colder months.
Home Remedies to Skip
Not all home remedies are safe for eczema. Some can actually worsen symptoms and damage the skin barrier.
Essential oils
While often marketed as natural remedies, essential oils are highly concentrated and can cause irritation or allergic reactions, especially on compromised skin.
Botanical ingredients in creams
Plant-based ingredients may sound gentle, but many can trigger contact dermatitis in eczema-prone skin.
Olive oil for skin care
Despite its popularity, olive oil has been shown to disrupt the skin barrier and may worsen eczema symptoms.
Understanding things to avoid with eczema is just as important as knowing what helps.
Over-the-Counter Medication Options
After discussing remedies to skip, it’s helpful to focus on over-the-counter eczema treatments supported by dermatology organizations.
Topical hydrocortisone
Low-strength hydrocortisone creams can reduce redness and itching during mild flares. These should be used short-term and according to package instructions.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines may help reduce itching, particularly at night, though they do not treat eczema itself.
OTC treatments can be a helpful supplement but should not replace professional guidance, especially for moderate to severe disease.
Get Eczema Treatment Today
Managing eczema effectively requires a combination of professional care and consistent at-home practices. From natural remedies for eczema and daily habit adjustments to safe over-the-counter treatments, daily routines play a key role in controlling symptoms and preventing flares.
These strategies are meant to support—not replace—care from a dermatology provider. If your provider recommends treatments not listed here, it is important to follow their guidance. This article is intended to help inform your at-home eczema treatment and encourage productive conversations with your care team.
If your eczema is not improving, worsening, or interfering with daily life, scheduling a dermatology appointment can help you find an individualized treatment plan that works for you.
*Medical Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Dermatology Partners is not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outcomes resulting from reliance on this information.
Source
American Academy of Dermatology Association. (n.d.). How to treat eczema at home. https://www.aad.org/news/how-to-treat-eczema-at-home
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Home remedies for eczema. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/home-remedies-for-eczema
National Eczema Association. (n.d.). Over-the-counter treatments. https://nationaleczema.org/treatments/over-the-counter/